Cockroach_ClusterColor
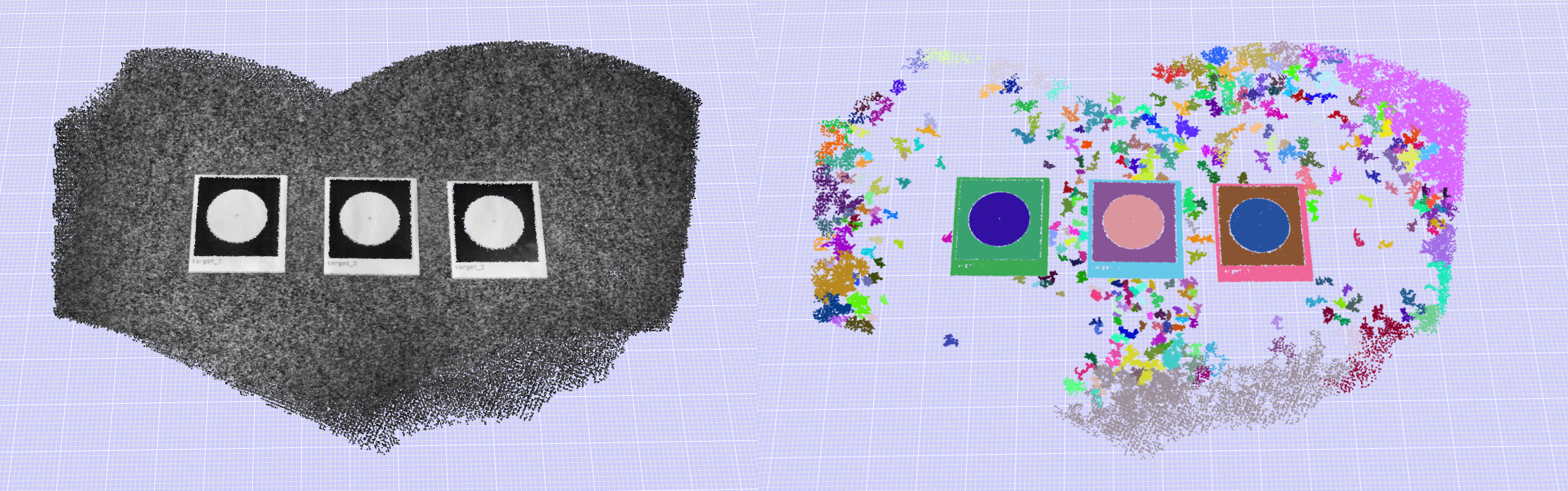
This is a clustering technique based on color. It will cluster the pointcloud based on the color of the points . It is often useful to cluster a pointcloud based on color to separate different colored component of a pointcloud. Note that this command can be used also with grayscale colors as in the image. As many clustering techniques the command uses a KNNsearch to find the colors relations of neighbors of each point.
The main algorithm is based on the Connected Component Extractor with a color proximity evaluator from the function in cilantro::ConnectedComponentExtraction3f().
Command options:
KSearch=30
The number of neighbours for each point to evaluate. The bigger the value, the more accurate the algorithm will be but the slower it will be.
MinClusterSize=100
The minimum number of points that a cluster should have to be considered as a cluster. The smaller the value, the more clusters will be detected.
DistanceThresholdColor=5
This parameters will define the color proximity between two points. The smaller the value, the more, smaller clusters will be detected. If the pointcloud is colored, each point carries one property of the color values as a vector of 3 values (RGB) ranging from 0 to 255: e.g. red=(255,0,0). The distance between two points is calculated as the euclidean distance between the two vectors. If the pointcloud is grayscale, the distance is calculated as the absolute difference between the two values. In sum, if you want to catch all the color nuances into seperate clusters, you should set a small value for this parameter.
ColorPointCloud=True
Decide with True/False whether to color the output group of clusters with random colors of keep the original colors.