Rotation
Geometric definition
A rotation is a transformation that turns a geometry around an axis by a certain angle. The angle can be defined in degrees or radians.
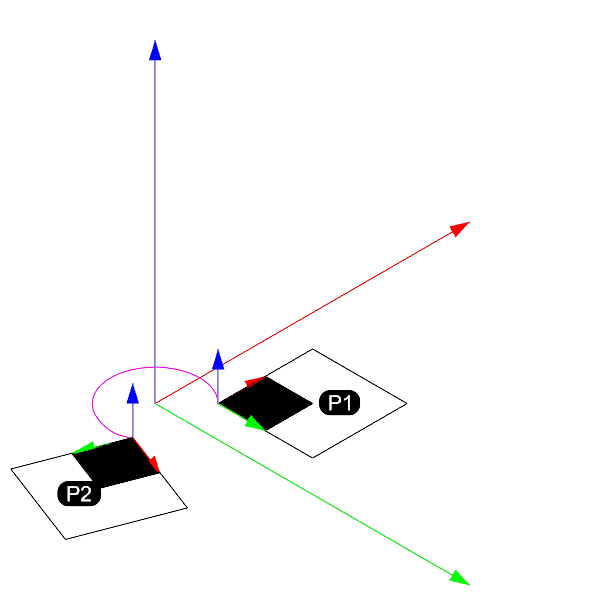
How to add
As often is possible in Rhino to use either RhinoCommons or RhinoScriptSynthax to add a point to the Rhino workspace. Here are the two methods:
RhinoCommons
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import scriptcontext as sc
import math as m
# create a rectangle
rectangle = rg.Rectangle3d(rg.Plane.WorldXY, 10, 10)
# create a rotation transformation with RhinoCommon
angle_degrees = 45
angle_radians = m.radians(angle_degrees)
rotation = rg.Transform.Rotation(angle_radians, # angle in radians
rg.Vector3d.ZAxis, # rotation axis
rg.Point3d.Origin) # rotation center
# transform the rectangle with RhinoCommon
rectangle.Transform(rotation)
# add the rectangle to the document
sc.doc.Objects.AddRectangle(rectangle)
RhinoScriptSynthax
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
# create a rectangle
rectangle_id = rs.AddRectangle(rs.WorldXYPlane(), 10, 10)
# create a rotation transformation
rotation = rs.XformRotation2(
45, # angle of rotation in degrees
[0, 0, 1], # axis of rotation
[0, 0, 0] # center of rotation
)
# transform the rectangle
rs.TransformObject(rectangle_id, rotation, copy=True)
Main methods and properties
Operators
Rotations as all the other transformations have a set of operators that can be used to perform to combine transformations (also different kinds, e.g.: translation with rotation). Here are the main ones:
xform_1 = rg.Transform.Rotation(m.radians(45), rg.Vector3d.ZAxis, rg.Point3d.Origin)
xform_2 = rg.Transform.Rotation(m.radians(45), rg.Vector3d.XAxis, rg.Point3d.Origin)
xform_3 = xform_2 * xform_1 # Will combine the two transformations
⚠️ Note that the order of the transformations is important. In the example above
xform_1will be applied first andxform_2will be applied second. ⚠️
Properties
Rotations as all the other transformations have a set of properties that can be used to retrieve information about the transformation. Here are the main ones:
rotation = rg.Transform.Rotation(m.radians(45), rg.Vector3d.ZAxis, rg.Point3d.Origin)
rotation.IsIdentity # Will return True if the transformation is an identity transformation
rotation.IsZero # Will return True if the transformation is a zero transformation
rotation.IsValid # Will return True if the transformation is valid
🛠 Exercises
Starting file:
01: 🦏⬇️⬇️⬇️ Download the file here ⬇️⬇️⬇️🦏 01: 🐍⬇️⬇️⬇️ Download the script here ⬇️⬇️⬇️🐍