python-I-collections
In Python, a collection is the other big family of datatypes for variables. These datatypes also called arrays they can contain mutliple values.
There are 4 types of collections and they have each one different modalities in which they are create and they operate with the data the contain.:
Lists
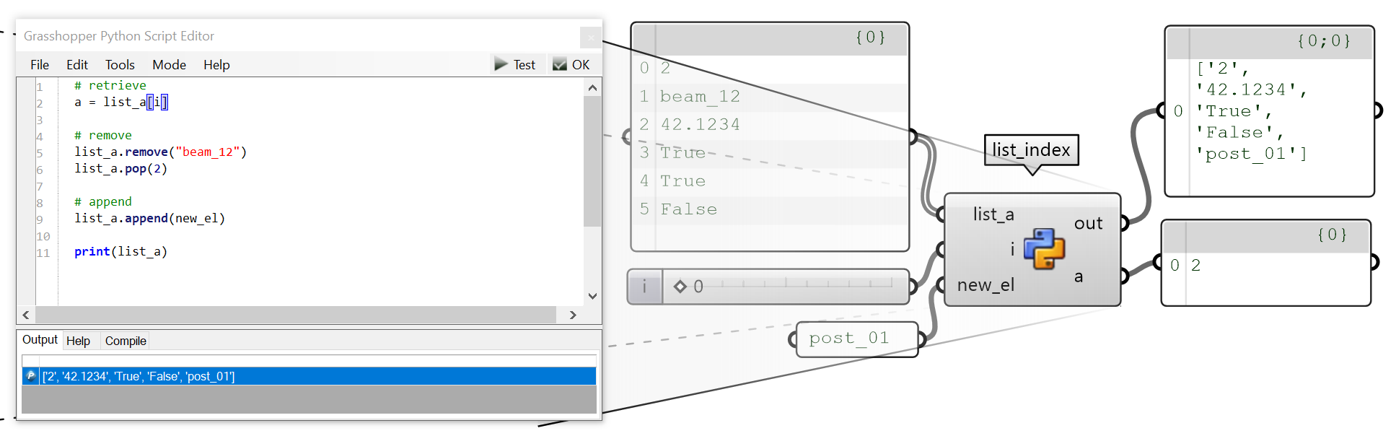
A list is a collection that is ordered and changeable. It allows to duplicate members.
# To create (instantiate)
a = [2,”beam_12”,42.1234,True,True,False]
# To retrieve an element
b = a[2] # 42.1234
# To remove an element
a.remove(“beam_12”)
a.pop(2)
# To insert an element
a.append(“post_01”)
Tuples
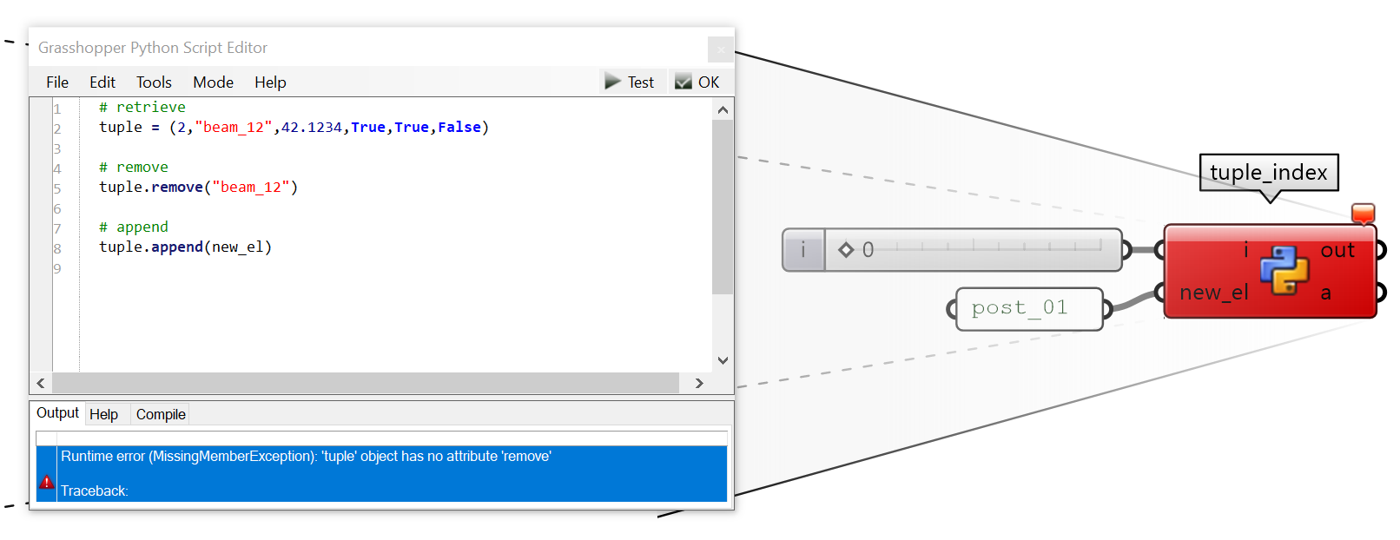
tuple is a collection that is ordered and unchangeable. It allows to duplicate members.
# To create (instantiate)
a = (2,”beam_12”,42.1234,True,True,False)
# To retrieve an element
b = a[2] # 42.1234
# To remove an element
impossible!
# To insert an element
impossible!
Sets
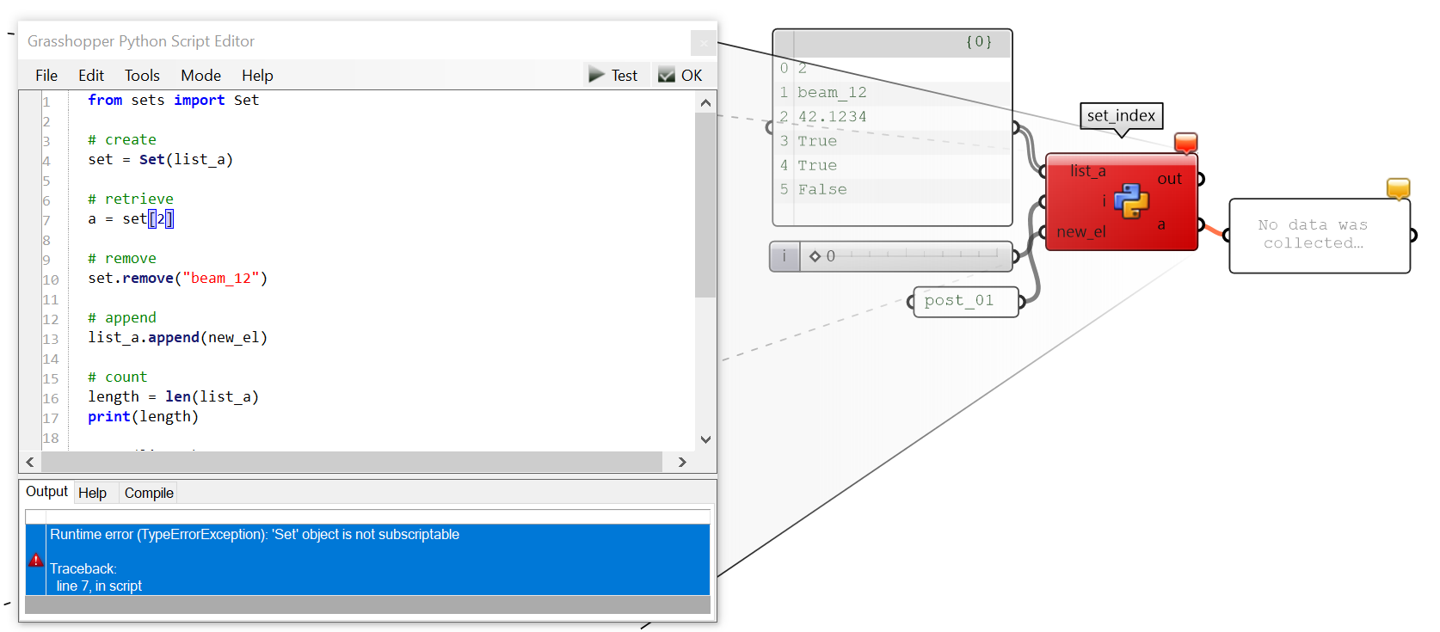
A set is a collection that is unordered and unchangeable* (in reality you can still add and remove elements). It does not allows to duplicate members.
# To create (instantiate)
a = {"a", "b"} # cannot have doubles!
# To retrieve an element
impossible! # only with list(a)[i]
# To remove an element
a.remove(“beam_12”)
# To insert an element
a.append(“post_01”)
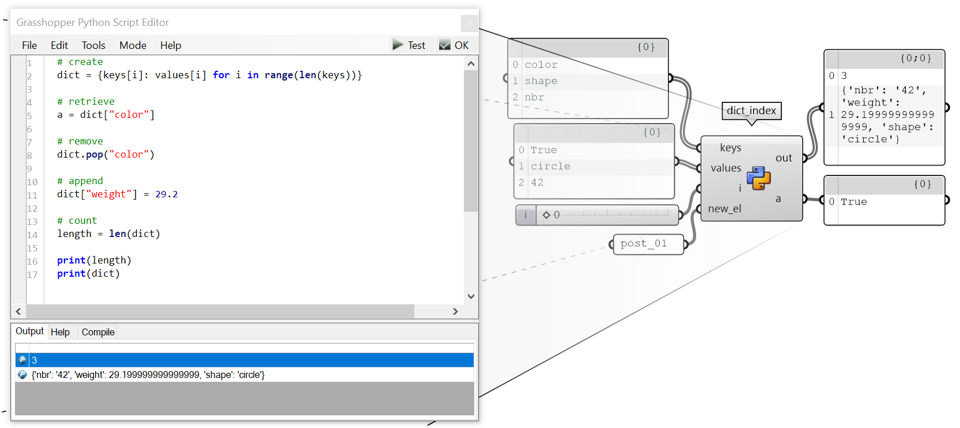
Dictionaries
dictionnary is a collection that is unordered* (After Python 3.7 dictionnaries are ordered, before they are unordered like in IronPython) and unchangeable. It does not allows to duplicate members. Each value of the dictionary is assigned a key.
# To create (instantiate)
dict = {“color”: True, “shape”: “circle”, “nbr”:42}
# To retrieve an element
b = dict[“color”] # True
# To remove an element
dict.pop(“color”)
# To insert an element
dict[“weight”] = 29.2
Collections can be used with a very powerfull tool in python: looping.