Inheritance
Inheritance is a way to create a new class from an existing class. The new class is called a subclass or child class. The existing class is called a superclass or parent class. The subclass inherits all the attributes and methods of the superclass. It can also add new attributes and methods or override existing ones. This is useful when we want to create a class that is similar to another class but with some additional features. It allows us to reuse code and avoid repetition. It also makes the code more readable and easier to maintain.
A superclass is often refered to as interface because it defines the interface of the subclass. It defines the attributes and methods that the subclass will have.
How to define inheritance
Here’s the superclass and sublcasses we will use in this example. All these beams can share some attributes (length, width, height) and methods (calculate_volume). The subclass can add new attributes and methods or override existing ones.
Beam (superclass)
├── GlulamBeam (subclass)
├── DuoBeam (subclass)
└── Log (subclass)
Superclass
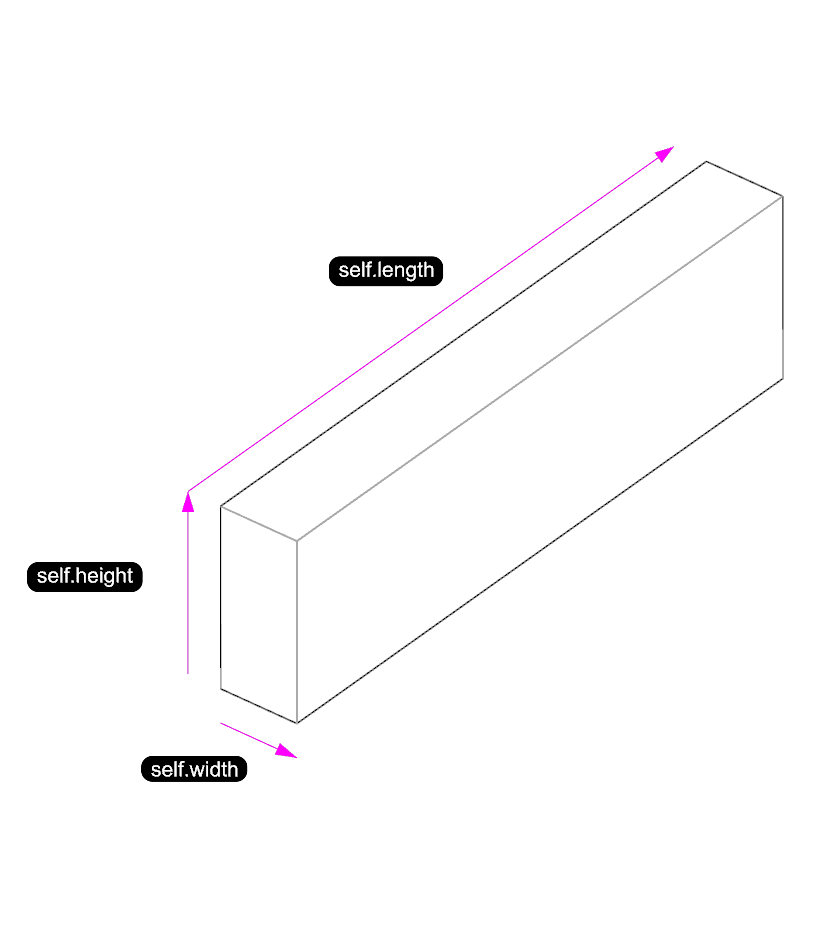
class Beam:
def __init__(self, length=2, width=0.2, height=0.5):
self.length = length
self.width = width
self.height = height
def calculate_volume(self):
return self.length * self.width * self.height
Subclass - DuoBeam
Basic example of inheritance. The DuoBeam class inherits all the attributes and methods of the Beam class.
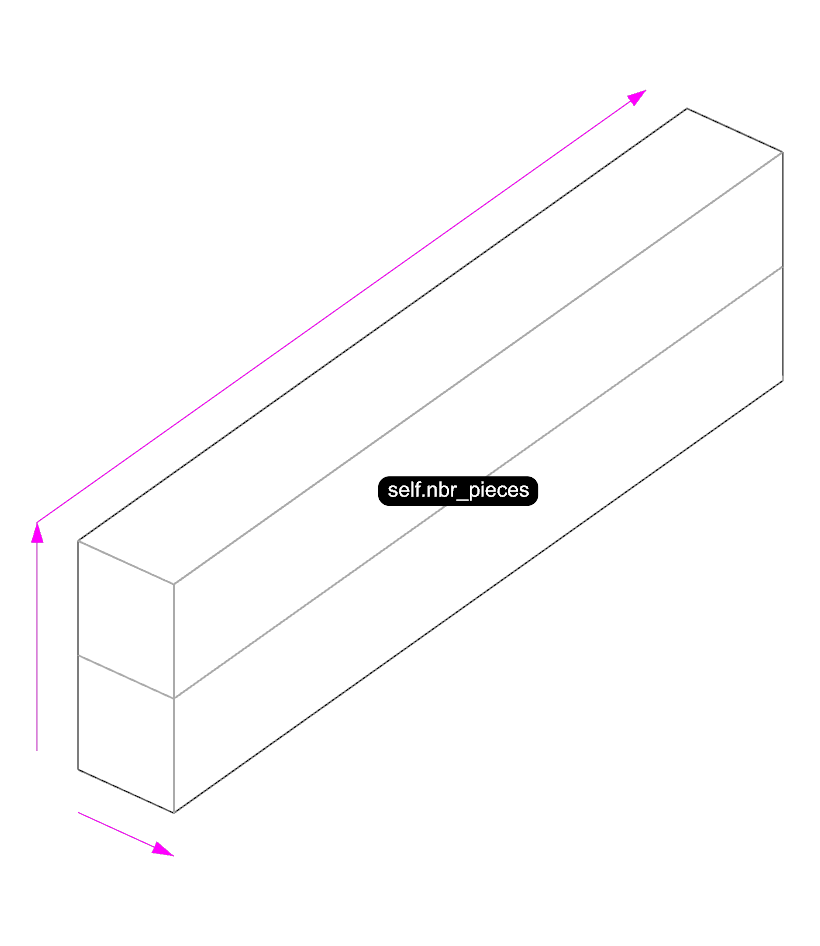
class DuoBeam(Beam):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.nbr_pieces = 2
my_duo = DuoBeam()
my_duo.calculate_volume()
Subclass - GlulamBeam
The GlulamBeam class inherits all the attributes and methods of the Beam class. It also adds a new attribute layers.
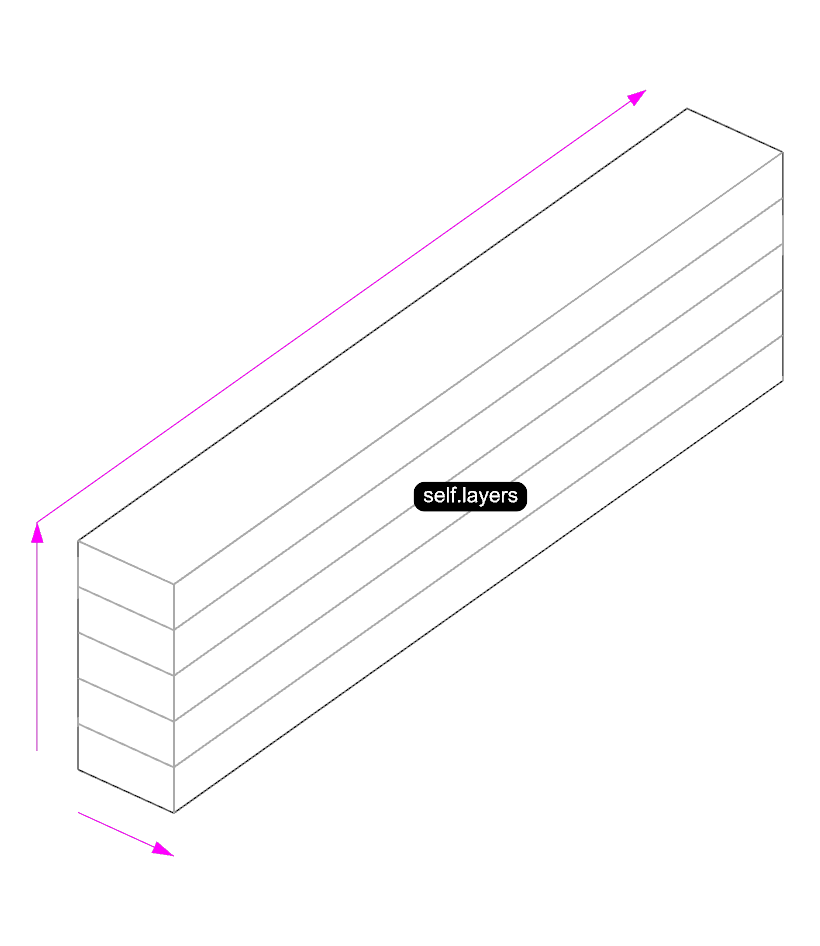
class GlulamBeam(Beam):
def __init__(self, layers):
super().__init__()
self.layers = layers
my_glulam = GlulamBeam(5)
print(my_glulam.calculate_volume())
Subclass - SolidBeam
In case of a SolidBeam, the width attribute is changed from the default value, this needs to be passed to the superclass’s constructor. Additionally The species attribute is added.
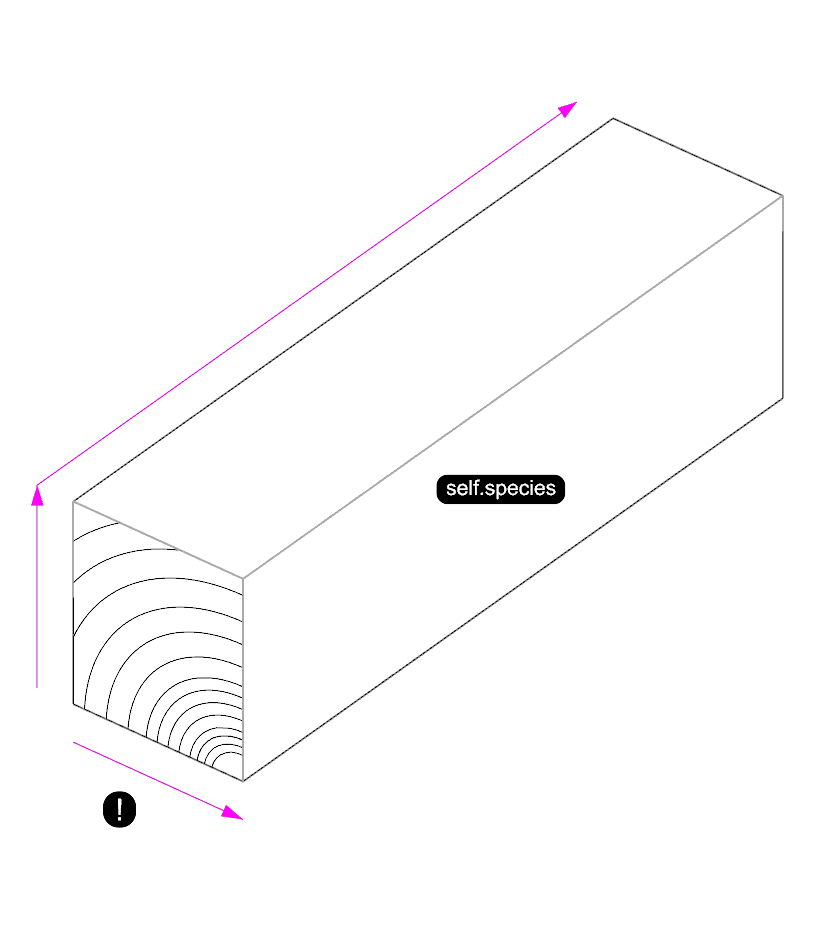
class SolidBeam(Beam):
def __init__(self, width, species): # width is changed from the default value
super().__init__(width) # width is changing from the default value
self.species = species
my_solid = SolidBeam(0.4, "oak")
print(my_solid.calculate_volume())
Subclass - Log
⚠️⚠️⚠️ You can still override the methods of the superclass. In case of a round log, the volume calculation is different. You should neverthless avoid this as it can lead to confusion. ⚠️⚠️⚠️
class LogBeam(Beam):
def __init__(self, radius):
super().__init__(width)
self.radius = radius
def calculate_volume(self): # overriding the method
return 3.14 * (self.width / 2) ** 2 * self.length
my_log = LogBeam(0.2)
print(my_log.calculate_volume())
🛠 Exercise
🐍⬇️⬇️⬇️ Download the script here ⬇️⬇️⬇️🐍
Solution:
🐍⬇️⬇️⬇️ Download the script here ⬇️⬇️⬇️🐍